Last week I wrote about increased conductivity in Múlakvísl glacier river that comes from Mýrdalsjökull glacier (Katla volcano). This trend has continued into second week with the conductivity. The conductivity in Múlakvísl is now on the range of ~327 to ~360 µS/cm. There has also been a slight increase in water levels following this change in Múlakvísl glacier river. Normal value for this time of year according to Icelandic Meteorological Office is ~180 µS/cm in Múlakvísl glacier river. Since 31-December-2013 the conductivity in Múlakvísl glacier river has always been over 220 µS/cm.
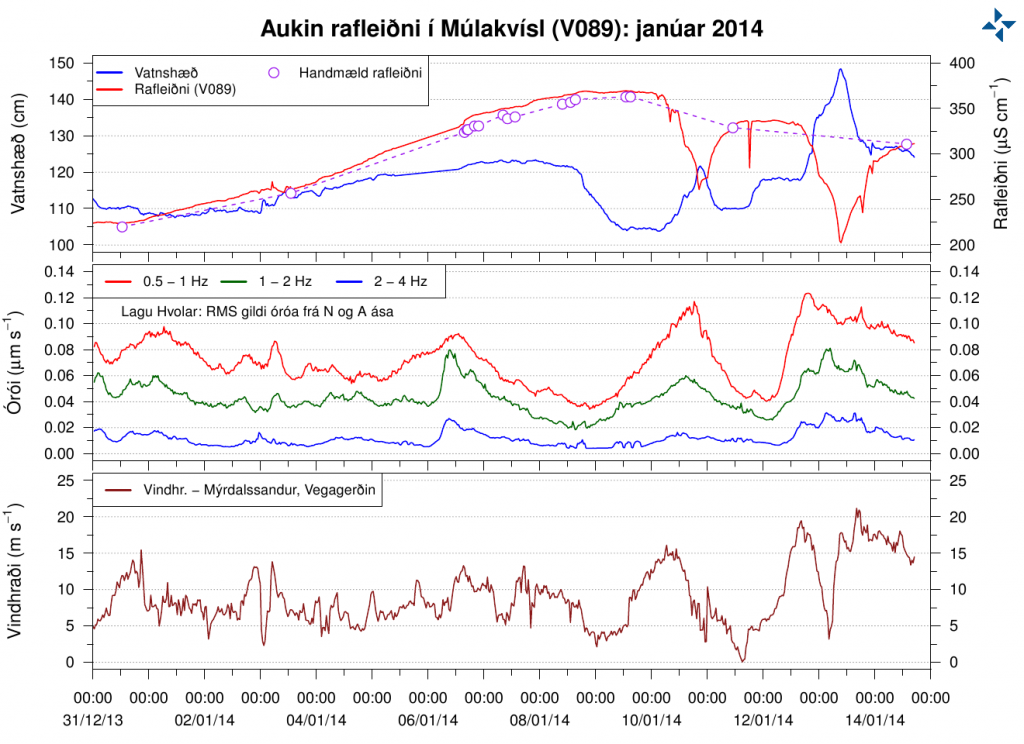
Conductivity in Múlakvísl glacier river. Top: conductivity. Middle: Harmonic tremor. Bottom: Windspeed. Copyright of this image belongs to Icelandic Meteorological Office.

Animated image from Icelandic Meteorological Office showing changes in Múlakvísl glacier river during this time period. Original image can be found here. Copyright of this image belongs to Icelandic Meteorological Office.
No harmonic tremors or earthquakes have been detected (besides normal activity) following this changes. What is taking place is that a cauldron in Mýrdalsjökull glacier is now leaking melt water that has been built up due to hydrothermal (hot springs) activity under the glacier. So far it does not appear that current changes in Múlakvísl glacier river mean anything at all. If that is going to change is impossible to know at this point.
Icelandic News about this
Rafleiðni há en enginn órói mælist (mbl.is)
Donation notice: Please remember to support me so that I can continue to report on volcano and earthquake activity in Iceland.
Post updated at 19:09 UTC on 15-January-2014.
Post updated at 20:49 UTC on 15-January-2014.

Any idea what is happening in Askja volcano? There is many weak magnitude quakes.
Askja volcano is quiet at the moment. This minor earthquakes so far don’t appear to mean anything.
The activity north-east of Askja volcano is normal for that area. It is highly active earthquake area that often has minor earthquake swarms. This earthquakes are tectonic in nature.