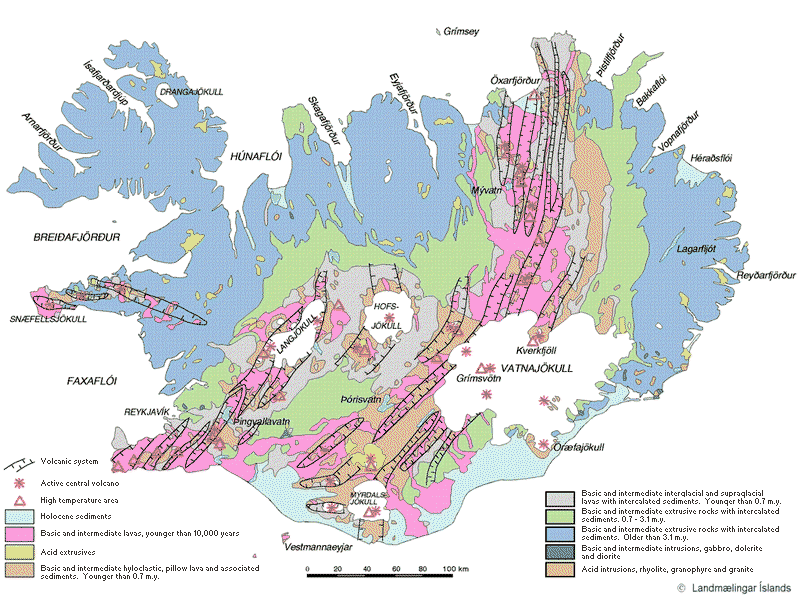
I have seen many speculations on how geology works in Iceland. Some of it is good and based on observation and factual basic. Other however is nothing but speculation and far from anything based on factual evidence on how geology works in Iceland.
Few right and wrong things about volcanism in Iceland
Volcano interaction Status: Limited truth to this
Volcano interaction is something of a debated among scientists. But what is not debated is the interaction between volcanoes that lies far apart. That interaction is none by it’s nature. So while I have been seeing discussion in the comments here that there is some connection between activity between Hengill volcano and Hekla volcano. This is untrue. There is no connection between those volcanoes and never has been. The reason is simple. The volcanoes are far apart. They don’t even share the same magma source. But that is evident by the lava that comes from this two volcanoes. But Hekla volcano has mixed types of eruption sometimes. But Hengill volcano only has Hawaii styles eruptions (if not hit by water) when it erupts, in style with other volcanoes on the Reykjanes ridge rift zone.
The only real life examples of volcano interaction are from Bárðarbunga volcano and Torfajökull volcano. The reason for this interaction is quite simple and logical one. Bárðarbunga fissure swarm cuts right trough Torfajökull volcano. When magma travels south-east in the fissure swarm (it last happened in the 15th century) it can hit the magma inside Torfajökull volcano. When this happens there is a big bang in Torfajökull volcano. As the magma in Torfajökull volcano seems to be colder and more Intermediate (andesitic) [link, Wikipedia] in nature. But in Bárðarbunga volcano the magma is Mafic (basaltic) in nature. When the two magmas mix, it ends with a bang and eruption in both volcanoes. But normally the process that starts this is because there is a ongoing eruption in Bárðarbunga volcano. So when Bárðarbunga volcano. I would worry about that rather then anything else.
See, no connection at all between Hekla and Hengill volcano. Copyright belongs too this picture owner. Owner unknown to me.
Iceland is going to have VEI-8 eruption. Status: Not likely.
All volcanoes can do a VEI-8. But the thing is that they are just not likely to do so. As the size of the eruption is directly connected to the inflow of magma it is getting. In the case of Icelandic volcanoes the inflow just seems to be few magnitude too small to make a VEI-8 eruption. The largest VEI eruption known in Iceland was a VEI-6 eruption that took place in Bárðarbunga volcano in the year 1477 (?).
As for VEI-8 eruption. I am not expecting that type of eruption any time soon in Iceland.
Iceland is one volcano. Status: False.
The simple answer is no. The long answer is. Iceland has many volcanoes, not just one. So the answer is no to this.
Geology in Iceland is well understood. Status: False
Geology in Iceland is understood. But far from being fully understood. As it happens geology science is just starting to now understand what complex progress are taking place in Iceland. A lot have been learned. But a lot more needs to be learned about how geology works in Iceland.
Volcano eruptions comes in active cycles. Status: True
This has been observed by actual data. But volcano activity happens in periods of 80 to 160 years. With a quiet period of 50 to 90 years. But numbers are approximation. During the quiet time there are fewer eruptions and they are smaller (hint: Large eruption can still happen however during the quiet period). Last quiet period started in around the year 1870 and did not end until the year 1983. But that year there was a eruption in Grímsfjall volcano. But then Grímsfjall volcano had not erupted since the year 1954, but that break was 29 years long for Grímsfjall volcano.
This graph here also shows this clearly. But this is volcanism in Iceland during the years 1875 and to the year 1993.
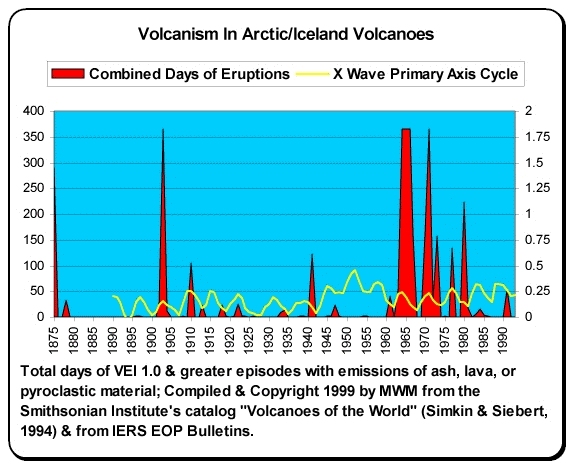
Copyright holder unknown. Copyright of this picture belongs to this owner.
It is impossible to know for sure when the high peak in the current cycle is going to be be. But most geologist are estimating that to be sometimes from the year 2020 and to 2080 or about that. So the years ahead is going to be quite busy in Iceland in the terms of volcano activity.
I am going to write more right and wrongs about Icelandic volcanoes soon. But for now this is good enough.
Sources and other things.
Volcano-tectonic Interaction in the Hengill Region, Iceland during 1993-1998 (pdf)
Volcano geodesy and magma dynamics in Iceland (ScienceDirect)
Interaction between Continental Lithosphere and the Iceland Plume—Sr-Nd-Pb Isotope Geochemistry of Tertiary Basalts, NE Greenland
Tomographic evidence for a narrow whole mantle plume below Iceland (ScienceDirect)
Pdf document on Hengill volcano crustal deformation.
Magma (Wikipedia)
Volcano geodesy and magma dynamics in Iceland (pdf)